01
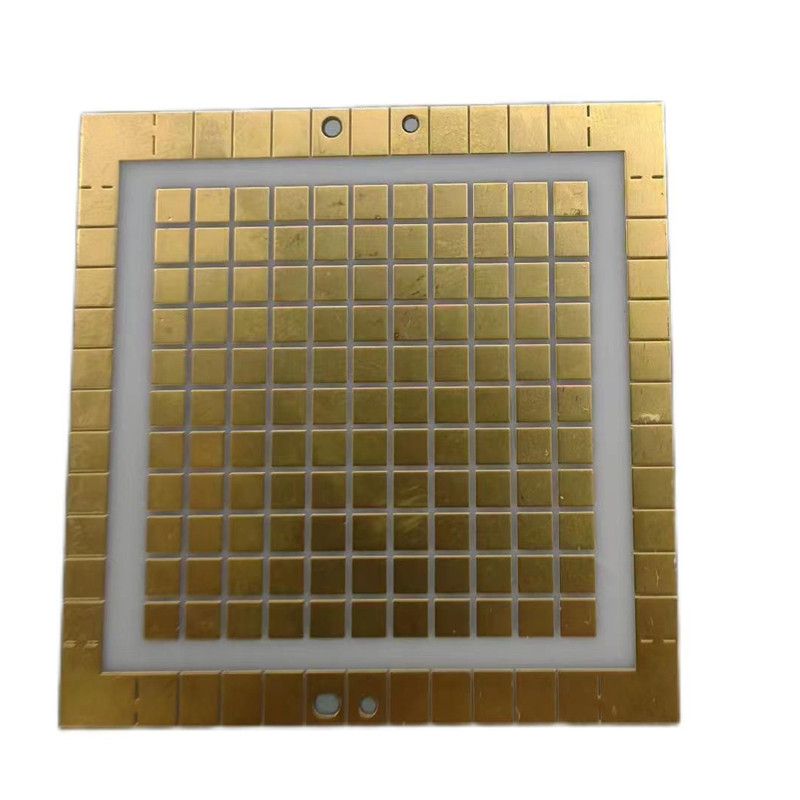
Ceramic Printed Circuit Boards
Main Ceramic PCB Types
From the level of substrates, ceramic PCBs include the aluminum, AIN, BeO, Si₃N₄, hybrid substrate boards, etc. From the layers of the circuit boards, there are the single-layer, double-layer, and multilayer.
Ceramic PCBs are usually made up of ceramic cores, with alumina and aluminum nitride (AIN) being two of the primary types. Both of these kinds of boards provide better thermal performance than metal core PCBs because there isn’t a need for an electric layer between the core and the circuits. Find out more about these two main kinds of ceramic PCB types below:
Advantages of Ceramic PCB
Safe operation in temperatures up to 350 degrees Celsius
Simple implementation of high-density circuit tracing
Exceptional high-frequency performance
Versatile packaging, with an option to come in hermetic packages to prevent water absorption
Tough chemical erosion resistance
Another ceramic PCB advantage is a lower overall system cost, which can be especially cost-effective for dense packages, since you have parallel processing of layers.